TCP parameters, Linux kernel
Updated on Wed, 2009-02-18 15:49. Originally created by jeromel on 2009-02-18 15:49.
TCP stack and signal
TCP call stack
The following flow graph represents the TCP socket client/server answer/reply flow stack.
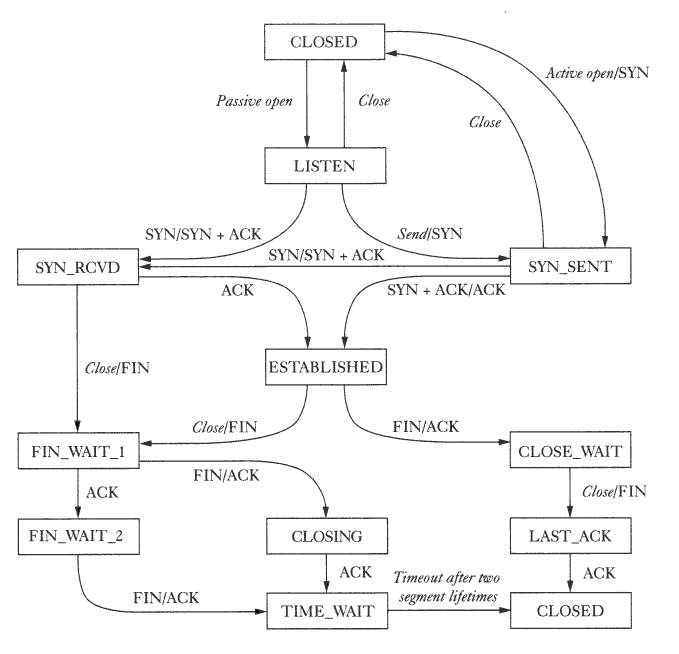
Termination of a connection goes to FIN_WAIT_1 -> FIN_WAIT_2 -> TIME_WAIT -> CLOSED. The move from TIME_WAIT to CLOSED is the ACK OR a TIME_WAIT state which is equal to 2*FIN.
Under LInux, one may change any parameters using a command such as
% echo "10" > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/tcp_fin_timeout % /etc/rc.d/init.d/network restart
It would set the TCP/FIN timeout to 10 seconds instead of its default 60 seconds.
You can also adjust the parameters in /etc/sysctl.conf ; in our example, the parameter is net.ipv4.tcp_fin_timeout.
List of TCP adjustable parameters and meaning
The below listing was extracted from this link.
/proc/sys/net/ipv4/* Variables: ip_forward - BOOLEAN 0 - disabled (default) not 0 - enabled Forward Packets between interfaces. This variable is special, its change resets all configuration parameters to their default state (RFC1122 for hosts, RFC1812 for routers) ip_default_ttl - INTEGER default 64 ip_no_pmtu_disc - BOOLEAN Disable Path MTU Discovery. default FALSE IP Fragmentation: ipfrag_high_thresh - INTEGER Maximum memory used to reassemble IP fragments. When ipfrag_high_thresh bytes of memory is allocated for this purpose, the fragment handler will toss packets until ipfrag_low_thresh is reached. ipfrag_low_thresh - INTEGER See ipfrag_high_thresh ipfrag_time - INTEGER Time in seconds to keep an IP fragment in memory. INET peer storage: inet_peer_threshold - INTEGER The approximate size of the storage. Starting from this threshold entries will be thrown aggressively. This threshold also determines entries' time-to-live and time intervals between garbage collection passes. More entries, less time-to-live, less GC interval. inet_peer_minttl - INTEGER Minimum time-to-live of entries. Should be enough to cover fragment time-to-live on the reassembling side. This minimum time-to-live is guaranteed if the pool size is less than inet_peer_threshold. Measured in jiffies. inet_peer_maxttl - INTEGER Maximum time-to-live of entries. Unused entries will expire after this period of time if there is no memory pressure on the pool (i.e. when the number of entries in the pool is very small). Measured in jiffies. inet_peer_gc_mintime - INTEGER Minimum interval between garbage collection passes. This interval is in effect under high memory pressure on the pool. Measured in jiffies. inet_peer_gc_maxtime - INTEGER Minimum interval between garbage collection passes. This interval is in effect under low (or absent) memory pressure on the pool. Measured in jiffies. TCP variables: tcp_syn_retries - INTEGER Number of times initial SYNs for an active TCP connection attempt will be retransmitted. Should not be higher than 255. Default value is 5, which corresponds to ~180seconds. tcp_synack_retries - INTEGER Number of times SYNACKs for a passive TCP connection attempt will be retransmitted. Should not be higher than 255. Default value is 5, which corresponds to ~180seconds. tcp_keepalive_time - INTEGER How often TCP sends out keepalive messages when keepalive is enabled. Default: 2hours. tcp_keepalive_probes - INTEGER How many keepalive probes TCP sends out, until it decides that the connection is broken. Default value: 9. tcp_keepalive_interval - INTEGER How frequently the probes are send out. Multiplied by tcp_keepalive_probes it is time to kill not responding connection, after probes started. Default value: 75sec i.e. connection will be aborted after ~11 minutes of retries. tcp_retries1 - INTEGER How many times to retry before deciding that something is wrong and it is necessary to report this suspection to network layer. Minimal RFC value is 3, it is default, which corresponds to ~3sec-8min depending on RTO. tcp_retries2 - INTEGER How may times to retry before killing alive TCP connection. RFC1122 says that the limit should be longer than 100 sec. It is too small number. Default value 15 corresponds to ~13-30min depending on RTO. tcp_orphan_retries - INTEGER How may times to retry before killing TCP connection, closed by our side. Default value 7 corresponds to ~50sec-16min depending on RTO. If you machine is loaded WEB server, you should think about lowering this value, such sockets may consume significant resources. Cf. tcp_max_orphans. tcp_fin_timeout - INTEGER Time to hold socket in state FIN-WAIT-2, if it was closed by our side. Peer can be broken and never close its side, or even died unexpectedly. Default value is 60sec. Usual value used in 2.2 was 180 seconds, you may restore it, but remember that if your machine is even underloaded WEB server, you risk to overflow memory with kilotons of dead sockets, FIN-WAIT-2 sockets are less dangerous than FIN-WAIT-1, because they eat maximum 1.5K of memory, but they tend to live longer. Cf. tcp_max_orphans. tcp_max_tw_buckets - INTEGER Maximal number of timewait sockets held by system simultaneously. If this number is exceeded time-wait socket is immediately destroyed and warning is printed. This limit exists only to prevent simple DoS attacks, you _must_ not lower the limit artificially, but rather increase it (probably, after increasing installed memory), if network conditions require more than default value. tcp_tw_recycle - BOOLEAN Enable fast recycling TIME-WAIT sockets. Default value is 1. It should not be changed without advice/request of technical experts. tcp_max_orphans - INTEGER Maximal number of TCP sockets not attached to any user file handle, held by system. If this number is exceeded orphaned connections are reset immediately and warning is printed. This limit exists only to prevent simple DoS attacks, you _must_ not rely on this or lower the limit artificially, but rather increase it (probably, after increasing installed memory), if network conditions require more than default value, and tune network services to linger and kill such states more aggressively. Let me to remind again: each orphan eats up to ~64K of unswappable memory. tcp_abort_on_overflow - BOOLEAN If listening service is too slow to accept new connections, reset them. Default state is FALSE. It means that if overflow occurred due to a burst, connection will recover. Enable this option _only_ if you are really sure that listening daemon cannot be tuned to accept connections faster. Enabling this option can harm clients of your server. tcp_syncookies - BOOLEAN Only valid when the kernel was compiled with CONFIG_SYNCOOKIES Send out syncookies when the syn backlog queue of a socket overflows. This is to prevent against the common 'syn flood attack' Default: FALSE Note, that syncookies is fallback facility. It MUST NOT be used to help highly loaded servers to stand against legal connection rate. If you see synflood warnings in your logs, but investigation shows that they occur because of overload with legal connections, you should tune another parameters until this warning disappear. See: tcp_max_syn_backlog, tcp_synack_retries, tcp_abort_on_overflow. syncookies seriously violate TCP protocol, do not allow to use TCP extensions, can result in serious degradation of some services (f.e. SMTP relaying), visible not by you, but your clients and relays, contacting you. While you see synflood warnings in logs not being really flooded, your server is seriously misconfigured. tcp_stdurg - BOOLEAN Use the Host requirements interpretation of the TCP urg pointer field. Most hosts use the older BSD interpretation, so if you turn this on Linux might not communicate correctly with them. Default: FALSE tcp_max_syn_backlog - INTEGER Maximal number of remembered connection requests, which are still did not receive an acknowledgement from connecting client. Default value is 1024 for systems with more than 128Mb of memory, and 128 for low memory machines. If server suffers of overload, try to increase this number. Warning! If you make it greater than 1024, it would be better to change TCP_SYNQ_HSIZE in include/net/tcp.h to keep TCP_SYNQ_HSIZE*16<=tcp_max_syn_backlog and to recompile kernel. tcp_window_scaling - BOOLEAN Enable window scaling as defined in RFC1323. tcp_timestamps - BOOLEAN Enable timestamps as defined in RFC1323. tcp_sack - BOOLEAN Enable select acknowledgments (SACKS). tcp_fack - BOOLEAN Enable FACK congestion avoidance and fast restransmission. The value is not used, if tcp_sack is not enabled. tcp_dsack - BOOLEAN Allows TCP to send "duplicate" SACKs. tcp_ecn - BOOLEAN Enable Explicit Congestion Notification in TCP. tcp_reordering - INTEGER Maximal reordering of packets in a TCP stream. Default: 3 tcp_retrans_collapse - BOOLEAN Bug-to-bug compatibility with some broken printers. On retransmit try to send bigger packets to work around bugs in certain TCP stacks. tcp_wmem - vector of 3 INTEGERs: min, default, max min: Amount of memory reserved for send buffers for TCP socket. Each TCP socket has rights to use it due to fact of its birth. Default: 4K default: Amount of memory allowed for send buffers for TCP socket by default. This value overrides net.core.wmem_default used by other protocols, it is usually lower than net.core.wmem_default. Default: 16K max: Maximal amount of memory allowed for automatically selected send buffers for TCP socket. This value does not override net.core.wmem_max, "static" selection via SO_SNDBUF does not use this. Default: 128K tcp_rmem - vector of 3 INTEGERs: min, default, max min: Minimal size of receive buffer used by TCP sockets. It is guaranteed to each TCP socket, even under moderate memory pressure. Default: 8K default: default size of receive buffer used by TCP sockets. This value overrides net.core.rmem_default used by other protocols. Default: 87380 bytes. This value results in window of 65535 with default setting of tcp_adv_win_scale and tcp_app_win:0 and a bit less for default tcp_app_win. See below about these variables. max: maximal size of receive buffer allowed for automatically selected receiver buffers for TCP socket. This value does not override net.core.rmem_max, "static" selection via SO_RCVBUF does not use this. Default: 87380*2 bytes. tcp_mem - vector of 3 INTEGERs: min, pressure, max low: below this number of pages TCP is not bothered about its memory appetite. pressure: when amount of memory allocated by TCP exceeds this number of pages, TCP moderates its memory consumption and enters memory pressure mode, which is exited when memory consumtion falls under "low". high: number of pages allowed for queueing by all TCP sockets. Defaults are calculated at boot time from amount of available memory. tcp_app_win - INTEGER Reserve max(window/2^tcp_app_win, mss) of window for application buffer. Value 0 is special, it means that nothing is reserved. Default: 31 tcp_adv_win_scale - INTEGER Count buffering overhead as bytes/2^tcp_adv_win_scale (if tcp_adv_win_scale > 0) or bytes-bytes/2^(-tcp_adv_win_scale), if it is <= 0. Default: 2 ip_local_port_range - 2 INTEGERS Defines the local port range that is used by TCP and UDP to choose the local port. The first number is the first, the second the last local port number. Default value depends on amount of memory available on the system: > 128Mb 32768-61000 < 128Mb 1024-4999 or even less. This number defines number of active connections, which this system can issue simultaneously to systems not supporting TCP extensions (timestamps). With tcp_tw_recycle enabled (i.e. by default) range 1024-4999 is enough to issue up to 2000 connections per second to systems supporting timestamps. icmp_echo_ignore_all - BOOLEAN icmp_echo_ignore_broadcasts - BOOLEAN If either is set to true, then the kernel will ignore either all ICMP ECHO requests sent to it or just those to broadcast/multicast addresses, respectively. icmp_destunreach_rate - INTEGER icmp_paramprob_rate - INTEGER icmp_timeexceed_rate - INTEGER icmp_echoreply_rate - INTEGER (not enabled per default) Limit the maximal rates for sending ICMP packets to specific targets. 0 to disable any limiting, otherwise the maximal rate in jiffies(1) See the source for more information. icmp_ignore_bogus_error_responses - BOOLEAN Some routers violate RFC 1122 by sending bogus responses to broadcast frames. Such violations are normally logged via a kernel warning. If this is set to TRUE, the kernel will not give such warnings, which will avoid log file clutter. Default: FALSE (1) Jiffie: internal timeunit for the kernel. On the i386 1/100s, on the Alpha 1/1024s. See the HZ define in /usr/include/asm/param.h for the exact value on your system. conf/interface/*: conf/all/* is special and changes the settings for all interfaces. Change special settings per interface. log_martians - BOOLEAN Log packets with impossible addresses to kernel log. accept_redirects - BOOLEAN Accept ICMP redirect messages. default TRUE (host) FALSE (router) forwarding - BOOLEAN Enable IP forwarding on this interface. mc_forwarding - BOOLEAN Do multicast routing. The kernel needs to be compiled with CONFIG_MROUTE and a multicast routing daemon is required. proxy_arp - BOOLEAN Do proxy arp. shared_media - BOOLEAN Send(router) or accept(host) RFC1620 shared media redirects. Overrides ip_secure_redirects. default TRUE secure_redirects - BOOLEAN Accept ICMP redirect messages only for gateways, listed in default gateway list. default TRUE send_redirects - BOOLEAN Send redirects, if router. Default: TRUE bootp_relay - BOOLEAN Accept packets with source address 0.b.c.d destined not to this host as local ones. It is supposed, that BOOTP relay daemon will catch and forward such packets. default FALSE Not Implemented Yet. accept_source_route - BOOLEAN Accept packets with SRR option. default TRUE (router) FALSE (host) rp_filter - BOOLEAN 1 - do source validation by reversed path, as specified in RFC1812 Recommended option for single homed hosts and stub network routers. Could cause troubles for complicated (not loop free) networks running a slow unreliable protocol (sort of RIP), or using static routes. 0 - No source validation. Default value is 0. Note that some distributions enable it in startip scripts.
»
- jeromel's blog
- Login or register to post comments