Lambda spin-spin correlations paper proposal
Title:
Observation of L-Lbar spin correlation in p+p collisions at RHIC
PAs:
Z. Tu, J. Vanek
Target journal:
PRL
Abstract:
About 50 years ago, it was discovered that L hyperons are produced polarized in collisions of unpolarized protons on beryllium. The origin of the polarization remains a mystery, but majority of results indicate that final-state effects may play an important role. An experimental method, developed at LEP in the late 90's, allows determination of spin composition of LLbar, LL, and LbarLbar pairs via measurement of L hyperon pair spin-spin correlations. We present results from the first experimental measurement of the L hyperon pair spin-spin correlations in p+p collisions at sqrt(s) = 200 GeV, collected by the STAR experiment in 2012. The pairs are reconstructed at mid-rapidity (|y| < 1) with 0.5 < p_T < 5.0 GeV/c for two different relative pair kinematics: In-cone (|Delta y| < 0.5 and |Delta phi| < pi/3) and Out-of-cone (0. 5 < |Delta y| < 2.0 or pi/3 < |Delta phi| < pi). The spin-spin correlation is found to be P_LL =(0.14 +- 0.03_stat +- 0.02_sys) for In-cone L-Lbar pairs which indicates that the L-Lbar pairs are spin-triplet dominated. This is in contrast with spin singlet dominance expected from the partonic level. The In-cone LL and LbarLbar pairs, and all Out-of-cone pairs are consistent with zero spin-spin correlation which corresponds to random spin mixture.
Conclusions:
We observed for the first time an indication of positive spin-spin correlation of L-Lbar pairs, P_LL =(0.14 +- 0.03_stat +- 0.02_sys), in p+p collisions at 200 GeV, collected by the STAR experiment in 2012. The positive correlation implies that the pairs more often carry the same sign of polarization.
The result hints an enhancement of the spin triplet states for the short-range L-Lbar pairs, while spin singlet state is expected from the partonic level s-sbar pairs, produced predominantly through non-perturbative processes. We found no spin correlation for long-range pairs.
This indicates that the hadronization process tends to generate polarization at the final state, washing out the memory of the partonic spin composition information.
This dynamical generation of polarization provides important experimental constraints on the models for describing lambda polarization, spin transfers, etc.
Paper draft
The paper draft is available here and below in the attachments of this page.
Analysis note
The analysis note is available here and below in the file attachments of this page.
Analysis codes
Available on CVS: cvs checkout offline/paper/psn0848
Answers to Spin PWG Comments
File with replies to Spin PWG comments is available here.
Figures:
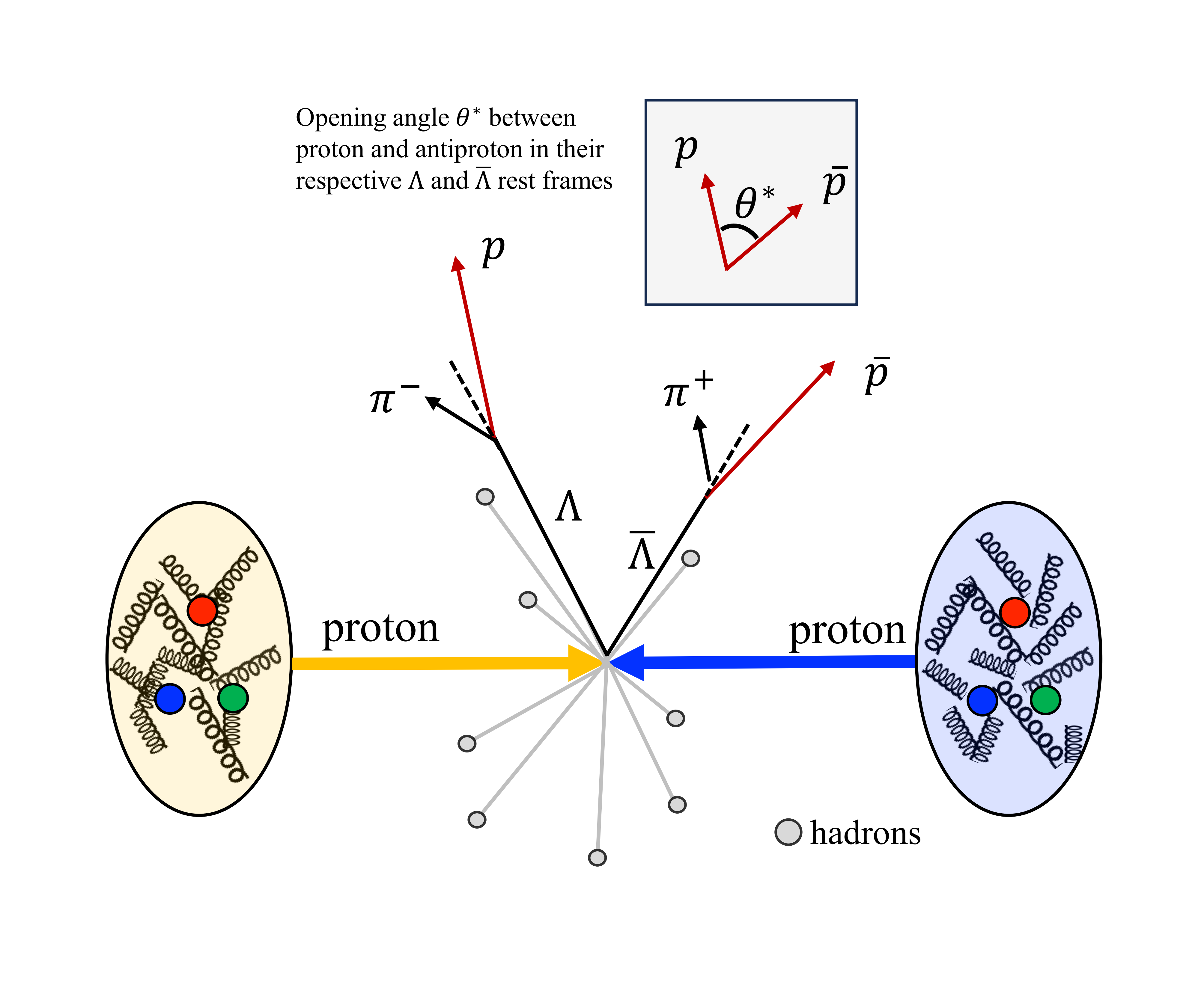
Figure 0: Illustration L-Lbar hyperon spin correlation in p+p collisions at RHIC.
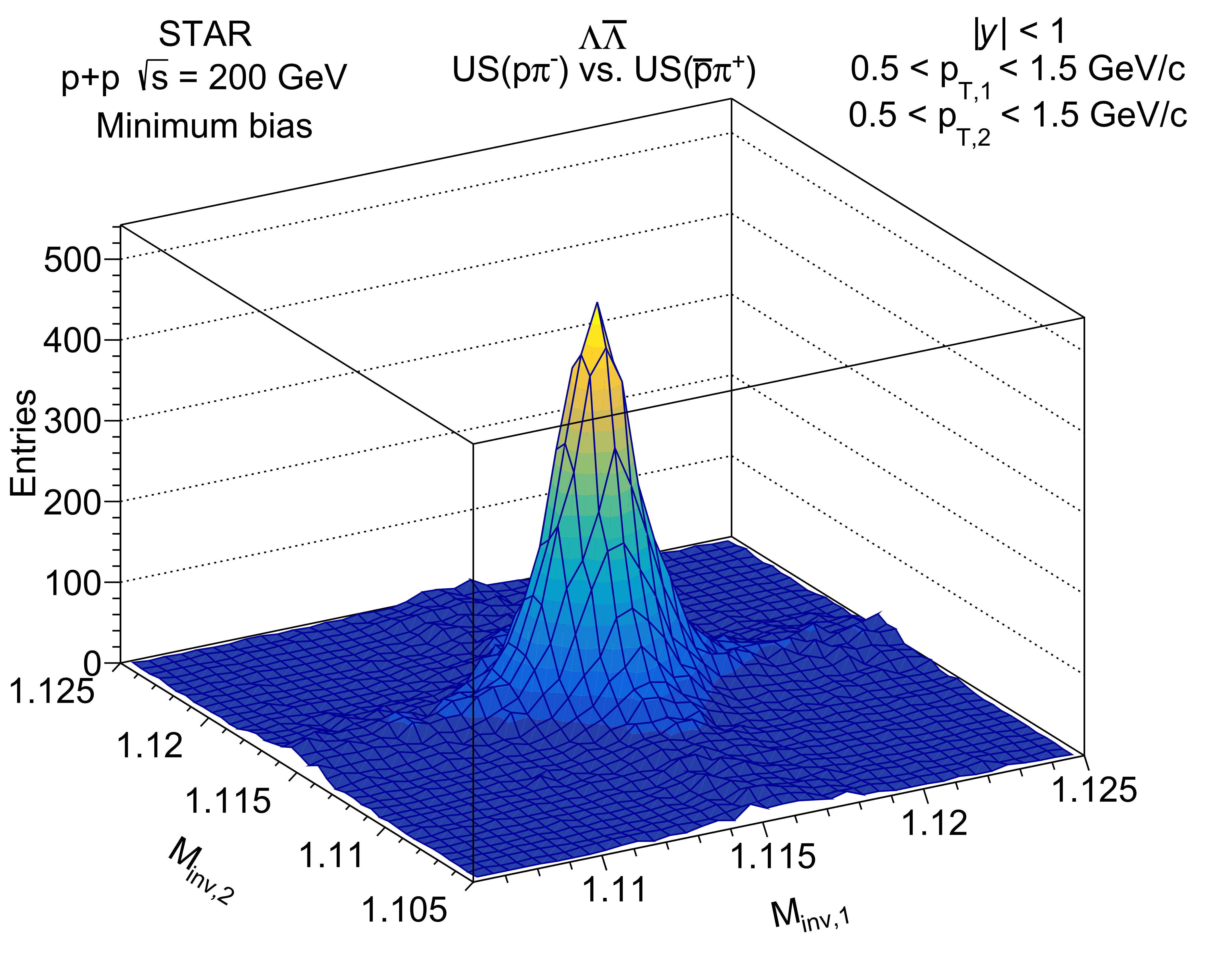
Figure 1: 2D invariant mass of pi-p pairs, paired with pi+pbar pairs. The true L-Lbar pairs are visible as the main peak in the middle of the plot. The two ridges then correspond to a real L or Lbar matched with combinatorial background. The main peak and both ridges are on top of a continuum background that originates from background pi-p pairs paired with background pi+pbar pairs.
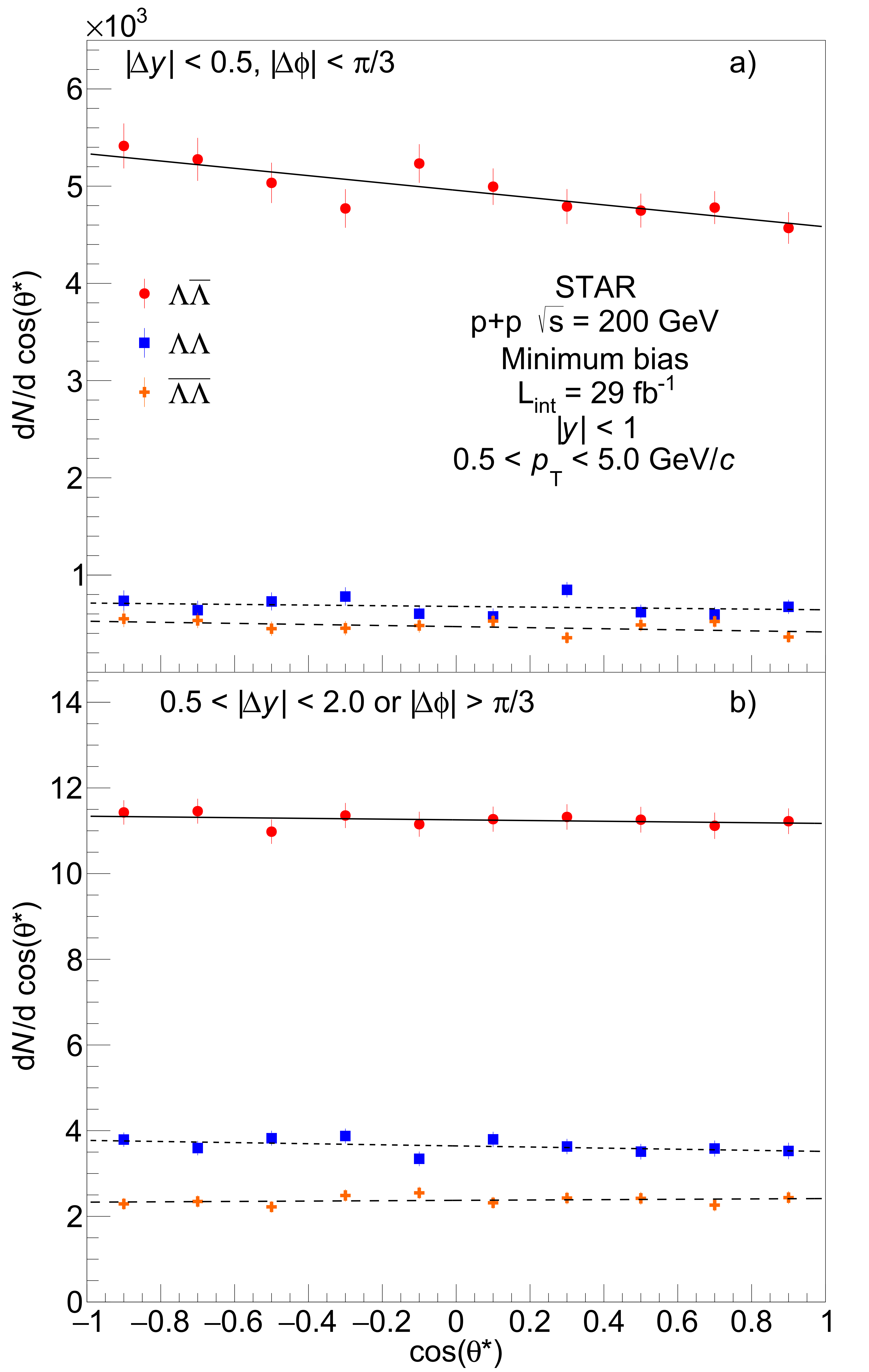
Figure 2: dN/dcos(theta*) distributions of decay (anti-)protons for LLbar, LL, and LbarLbar hyperon pairs measured at mid-rapidity (|y| < 1). Panel a) shows the short-range pairs (|Delta y| < 0.5 and |Delta phi| < pi/3) and panel b) shows the long-range pairs. The fits to the data are used to extract the corresponding spin-spin correlation values P_L1L2.

Figure 3: Spin-spin correlation P_L1L2 of short-range (a)) and long-range (b)) LLbar, LL, and LbarLbar hyperon pairs. The hyperon pair P_L1L2 is compared to K0sK0s and PYTHIA baseline.
Supporting figures:
Supporting figures can be found here.
GPC meetings:
11/18/2024: Slides
PWGC preview:
08/09/2024: Slides
Spin PWG presentations:
11/09/2022: https://drupal.star.bnl.gov/STAR/system/files/20221109_Lambda_update_0.pdf
11/11/2022: https://drupal.star.bnl.gov/STAR/system/files/20221116_Lambda_update_final.pdf
02/28/2023: Collaboration meeting, Berkeley
03/08/2023: https://drupal.star.bnl.gov/STAR/system/files/20230308_L_spin_corr_preliminary_request.pdf
08/09/2023: https://drupal.star.bnl.gov/STAR/system/files/20230809_LL_spin_corr_update.pdf
09/13/2023: https://drupal.star.bnl.gov/STAR/system/files/20230913_L_spin_spin_corr_reliminiary_request.pdf
10/01/2023: https://drupal.star.bnl.gov/STAR/system/files/20231001_L_spin_spin_correlations.pdf
12/13/2023: https://drupal.star.bnl.gov/STAR/system/files/20231213_L_spin_spin_correlations.pdf
03/06/2024: https://drupal.star.bnl.gov/STAR/system/files/20240306_L_spin_spin_correlations.pdf
03/19/2024: Collaboration meeting, BNL
05/29/2024: https://drupal.star.bnl.gov/STAR/system/files/20240529_L_spin_spin_correlations.pdf
07/03/2024: https://drupal.star.bnl.gov/STAR/system/files/20240703_L_spin_spin_correlations.pdf
07/10/2024: https://drupal.star.bnl.gov/STAR/system/files/20240710_L_spin_spin_correlations.pdf
07/17/2024: https://drupal.star.bnl.gov/STAR/system/files/20240717_L_spin_spin_correlations.pdf
09/11/2024: https://drupal.star.bnl.gov/STAR/system/files/20240911_L_sipn_spin_correlations.pdf
- vanekjan's blog
- Login or register to post comments