Heavy Flavor
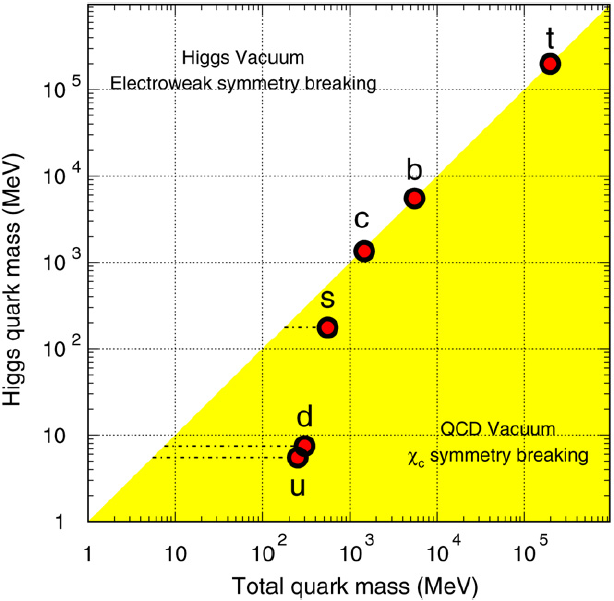 Depending on the energy scale, there are two mechanisms that generate quark masses with different degrees of importance: current quark masses are generated by the electroweak symmetry breaking mechanism (Higgs mass) and spontaneous chiral symmetry breaking leads to the constituent quark masses in QCD (QCD mass). The QCD interaction strongly affects the light quarks (u, d, s) while the heavy quark masses (c, b, t) are mainly determined by the Higgs mechanism. In high-energy nuclear collisions at RHIC, heavy quarks are produced through gluon fusion and qq¯ annihilation. Heavy quark production is also sensitive to the parton distribution function. Unlike the light quarks, heavy quark masses are not modified by the surrounding QCD medium (or the excitations of the QCD medium) and the value of their masses is much higher than the initial excitation of the system. It is these differences between light and heavy quarks in a medium that make heavy quarks an ideal probe to study the properties of the hot and dense medium created in high-energy nuclear collisions.
Depending on the energy scale, there are two mechanisms that generate quark masses with different degrees of importance: current quark masses are generated by the electroweak symmetry breaking mechanism (Higgs mass) and spontaneous chiral symmetry breaking leads to the constituent quark masses in QCD (QCD mass). The QCD interaction strongly affects the light quarks (u, d, s) while the heavy quark masses (c, b, t) are mainly determined by the Higgs mechanism. In high-energy nuclear collisions at RHIC, heavy quarks are produced through gluon fusion and qq¯ annihilation. Heavy quark production is also sensitive to the parton distribution function. Unlike the light quarks, heavy quark masses are not modified by the surrounding QCD medium (or the excitations of the QCD medium) and the value of their masses is much higher than the initial excitation of the system. It is these differences between light and heavy quarks in a medium that make heavy quarks an ideal probe to study the properties of the hot and dense medium created in high-energy nuclear collisions.
Heavy flavor analyses at STAR can be separated into quarkonia, open heavy flavor and heavy flavor leptons.
Updated spectra with new version of fastsim
Dpm spectra for centralities 0-10, 10-40, 40-80 and 0-80 with new binning (to match Guannan's D0) and new version of fast simulator. There is still a difference in pT dependence...
Plots obtained with BDT
Plots in the 2-6 GeV/c range for 0-10 % centrality obtained using BDT.
All pT and centrality bins - traditional analysis Dpm signal
Correct-sign and scaled wrong-sign combinations and signal plots after subtractions for all pT and centrality bins.
Update on analysis
Producing new files from picoDsts with loose cuts and all relevant information.
Next: BDT training and application, effectivityXacceptance calculation
D* production in p+p run 15, HF PWG 19 Jan 2017
D* production in p+p run 15, HF PWG 19 Jan 2017
Poster draft for QM17: D0 in Cu+Au
Versions:
02 - first draft
04 - improved draft: mainly typos and stylistics, first round of Institutional comments
05 - incorporated Institutional and PWG comments