Jet-like correlations
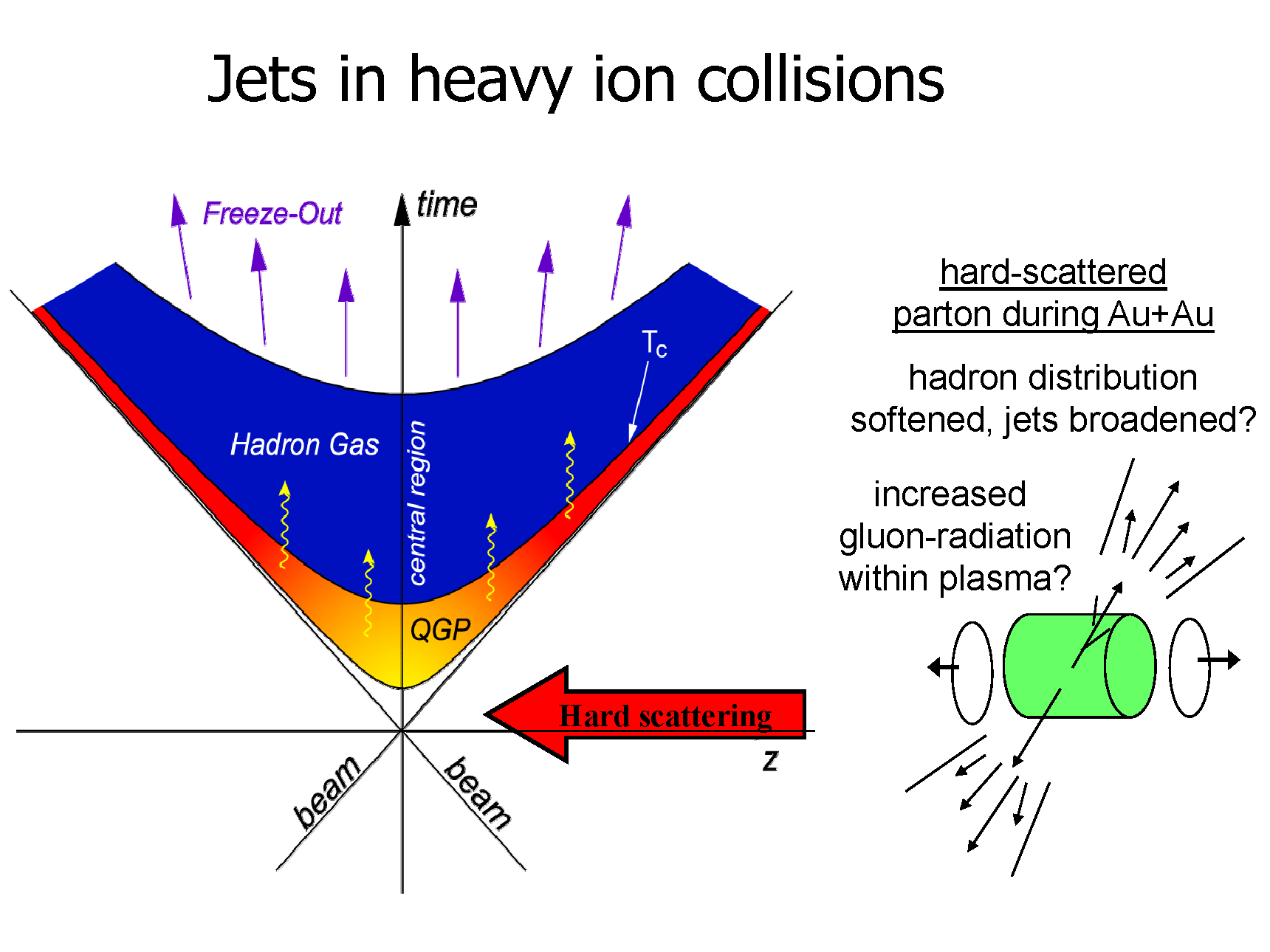
A jet is a spray of hadrons produced by the “hard” scattering of a parton (quark or gluon). A hard scattering is one in which a large amount of energy is transferred between partons.
Hard scatterings occur early in a heavy-ion collision, allowing the scattered partons to act as probes of the medium created in these collisions.
The modifications of jets measured in Au+Au collisions compared to p+p collisions is interpreted to be an effect of the large densities in Au+Au collisions. Such modifications have been measured in a variety of observables.
- Suppression of hadrons measured at high transverse momentum (pT)
- Suppression of the away-side jet measured in 2-particle correlations, when selecting a high pT trigger particle
Ongoing analyses in this Physics Working Group focus on correlations measured between particles to further understand jet modifications in the medium produced in Au+Au collisions. Such analyses include:
- Untriggered 2-particle correlation measurements in 2 dimensions
- Particle-identified particle correlations
- 2+1 correlation measurements
- Direct-photon-triggered correlations
- Studies of the long range correlation in pseudorapidity observed in central Au+Au collisions
- Full jet reconstruction
- High pT single-particle hadron measurements at lower beam energies
Groups:
- Printer-friendly version
- Login or register to post comments